一、简介
SpringBoot由众多的starter组成,这些starter也被称为是场景启动器,在工程中引入特定的starter再进行少量的配置就可以使用其提供的相应的功能了,SpringBoot在不断的维护和扩展不同场景的starter给使用者提供更完善的功能,我们也可以创建自定义的starter制定我们自己的特定场景。
二、SpringBoot中的starter
-
我们查看SpringBoot提供的starter可以发现所有的starter包下都没有任何代码
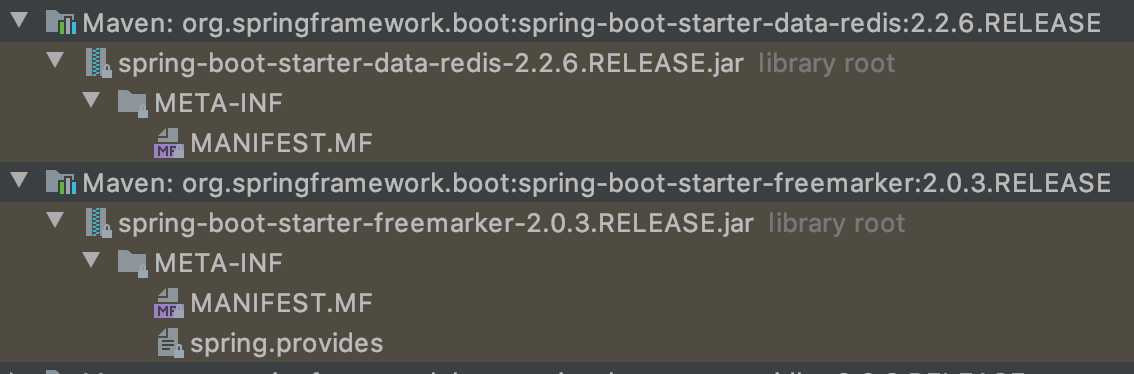
-
我们找到
spring-boot-starter-data-redis.jar包的pom.xml查看一下内容1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<name>Spring Boot Data Redis Starter</name>
<!-- 省略一部分 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>我们看到这个starter继承自
spring-boot-starters包,并且所有的starter都引入了spring-boot-starter包,包中还可以根据需要选择性的引入其他的jar包。 -
进入到
spring-boot-starter包中,可以找到它引入了spring-boot-autoconfigure包,这是我们完成自动配置的关键1
2
3
4
5
6<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>查看
spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar的目录结构发现包含了各种starter的配置信息。- 标1:需要自动配置的类声明文件
- 标2:配置文件中自动提示的元属性数据声明文件
- 标3:自动配置控制类
- 标4:场景属性类
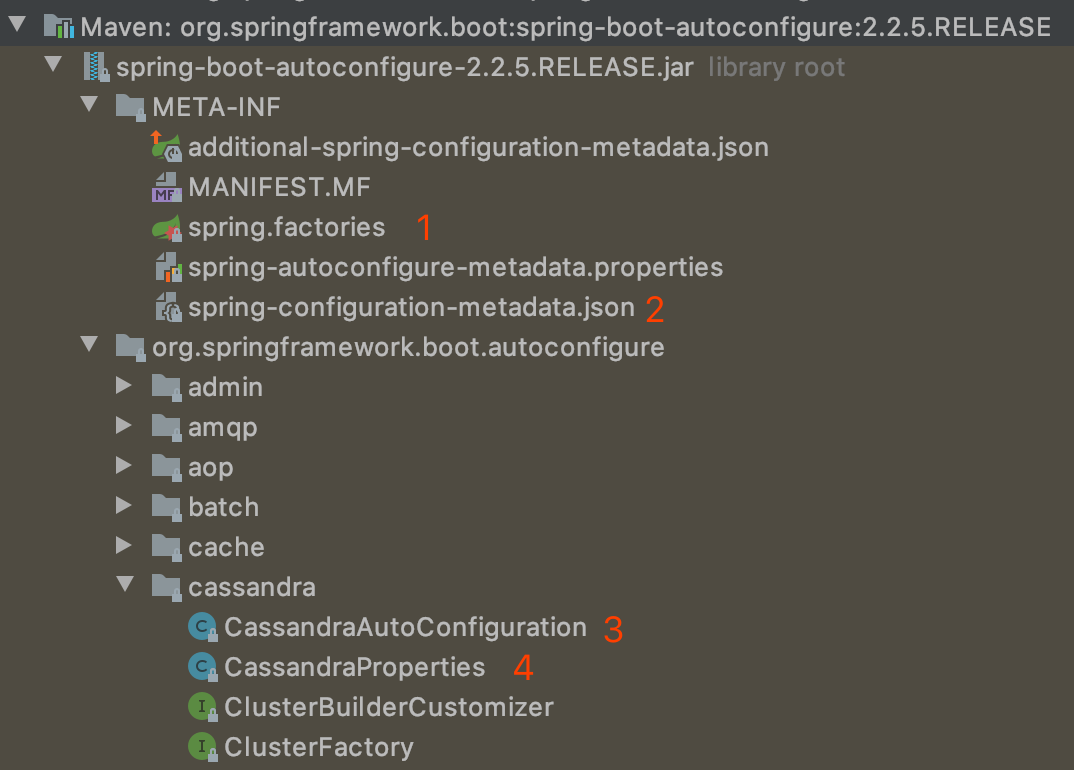
以上就是一个starter的关键所在了,总结下来就是:
- 启动器starter只是用来做依赖管理的,其不应该包含任何代码和配置,需要引入autoconfigure包
- 自动装配autoconfigure包,需要包含我们需要让SpringBoot自动装配的模块,以及资源配置信息,总的来说包括:spring.factories、spring-configuration-metadata.json、XxxAutoConfiguration、XxxProperties
- 使用的时候只需要引入启动器starter就可以实现自动配置
三、自定义starter命名规范
- 官方命名规范
- 规则:spring-boot-starter-模块名
- 举例:spring-boot-starter-data-redis、spring-boot-starter-web
- 自定义命名规范
- 规则:模块名-spring-boot-starter
- 举例:cc-spring-boot-starter
四、自定义starter demo
根据上面的描述,我们需要创建两个项目:cc-spring-boot-autoconfigure和cc-spring-boot-starter
-
创建cc-spring-boot-autoconfigure工程
需要注意的是在工程创建完成之后,要删除启动类、application.properties和test文件夹
-
pom.xml和控制类
-
pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>cc.lu</groupId>
<artifactId>cc-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project> -
CcProperties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42package cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
(prefix = "cc.config")
public class CcProperties {
private String name = "cc";
private Integer age = 3;
private String birthday;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(String birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String toString() {
return "CcProperties{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", birthday='" + birthday + '\'' + '}';
}
}类的有些属性被设置了值,这些值就是当配置文件未配置属性时使用的默认值,这就是参数配置设置默认值的一种方式。还有一种,继续往下看
-
CcService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15package cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt;
public class CcService {
private CcProperties ccProperties;
public void setCcProperties(CcProperties ccProperties) {
this.ccProperties = ccProperties;
}
public String info() {
return ccProperties.toString();
}
}一个普通的类,没啥可说的,继续往下
-
CcAutoConfiguration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28package cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
(proxyBeanMethods = false)
({ CcService.class })
({ CcProperties.class })
public class CcAutoConfiguration {
private CcProperties ccProperties;
({ CcService.class })
public CcService ccService() {
CcService ccService = new CcService();
// 打个日志查看方法是否被调用
System.out.println("------auto register!------");
ccService.setCcProperties(ccProperties);
return ccService;
}
}CcAutoConfiguration的声明上使用了@ConditionalOnClass和@EnableConfigurationProperties做加载控制,然后在类中创建了CcService的实例,并且使用
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ CcService.class })来控制创建条件。
-
-
spring.factories和spring-configuration-metadata.json配置
-
spring.factories
1
2=\
cc.lu.autoconfigurer.wt.CcAutoConfiguration将CcAutoConfiguration放给EnableAutoConfiguration,告知SpringBoot启动的时候进行检测加载。
-
spring-configuration-metadata.json元属性数据配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29{
"groups": [
{
"name": "cc.config",
"type": "cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt.CcProperties",
"sourceType": "cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt.CcProperties"
}
],
"properties": [
{
"name": "cc.config.age",
"type": "java.lang.Integer",
"sourceType": "cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt.CcProperties",
"defaultValue": 3
},
{
"name": "cc.config.birthday",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt.CcProperties"
},
{
"name": "cc.config.name",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "cc.lu.autoconfigure.wt.CcProperties",
"defaultValue": "cc"
}
],
"hints": []
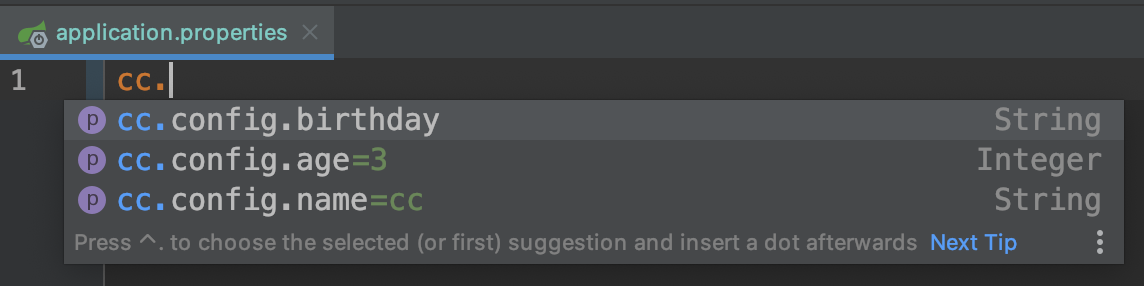
}这个文件的目的是在properties或yml文件中配置自定义属性的时候,可以自动提示,例如:
这个文件看上去好像非常复杂,尤其是当我们有几十个自定义配置属性的时候,难道要一个个属性的去写吗?答案是当然不用,可以通过引入一个jar包来在打包的时候自动生成:
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>引入之后,执行完命令
mvn clean package之后,到target/classes/META-INF目录下查看自动生成的文件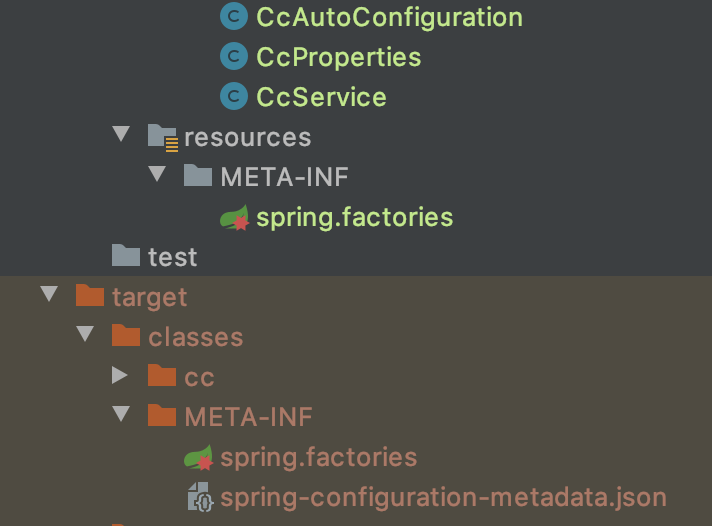
-
至此,我们的cc-spring-boot-autoconfigure就创建完成了,回瞄一眼,是不是和官方的autoconfigure包含的文件一致了。
-
-
创建cc-spring-boot-starter工程
一个很普通的maven工程,因为starter中一般不包含任何代码,仅仅作为包的依赖管理工程,所以创建完成之后依然要删除启动类、application.properties和test文件夹,它只有一个pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cc.lu</groupId>
<artifactId>cc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<name>cc-spring-boot-starter</name>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cc.lu</groupId>
<artifactId>cc-spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project> -
创建cc-starter-demo测试工程
创建一个常规的SpringBoot工程,引入我们自定义的starter,并设置相关的配置信息,就可以使用了。
-
pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>cc.lu</groupId>
<artifactId>cc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency> -
application.properties
修改birthday和name两个属性,age使用默认值,待会看效果
1
2=2017-03-09
=yc -
创建一个Controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20package cc.lu.starter.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import cc.lu.autoconfigurer.wt.CcService;
public class PersonController {
private CcService ccService;
("/info")
public void info() {
System.out.println(ccService.info());
}
}
-
五、测试
1. 情况一
-
启动cc-starter-demo工程,查看启动日志,会发现我们在CcAutoConfiguration中打印的字符串
------auto register!------出现在了控制台,说明CcService的实例创建是在CcAutoConfiguration中完成的。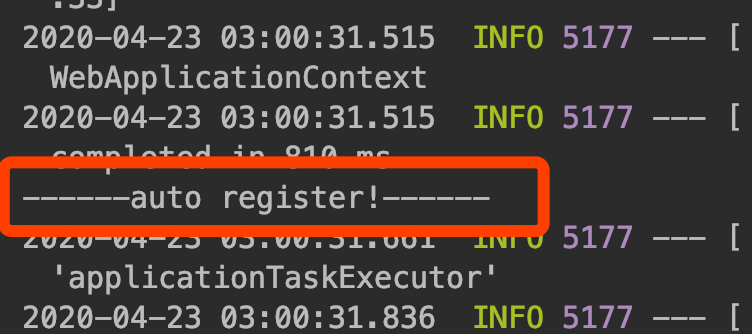
-
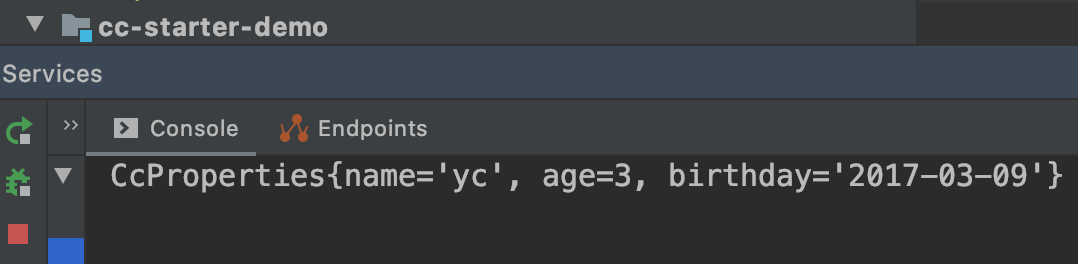
访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/info,查看控制台的日志,看到我们在application.properties文件中配置的值生效了,也就是我们的starter写的正常。
2. 情况二
-
在启动类中重新定义CcService的实例创建方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public CcService ccService(CcProperties ccProperties) {
CcService ccService = new CcService();
// 打个日志查看方法是否被调用
System.out.println("====client register====");
ccService.setCcProperties(ccProperties);
return ccService;
} -
启动工程,查看控制台是打印了字符串
====client register====还是------auto register!------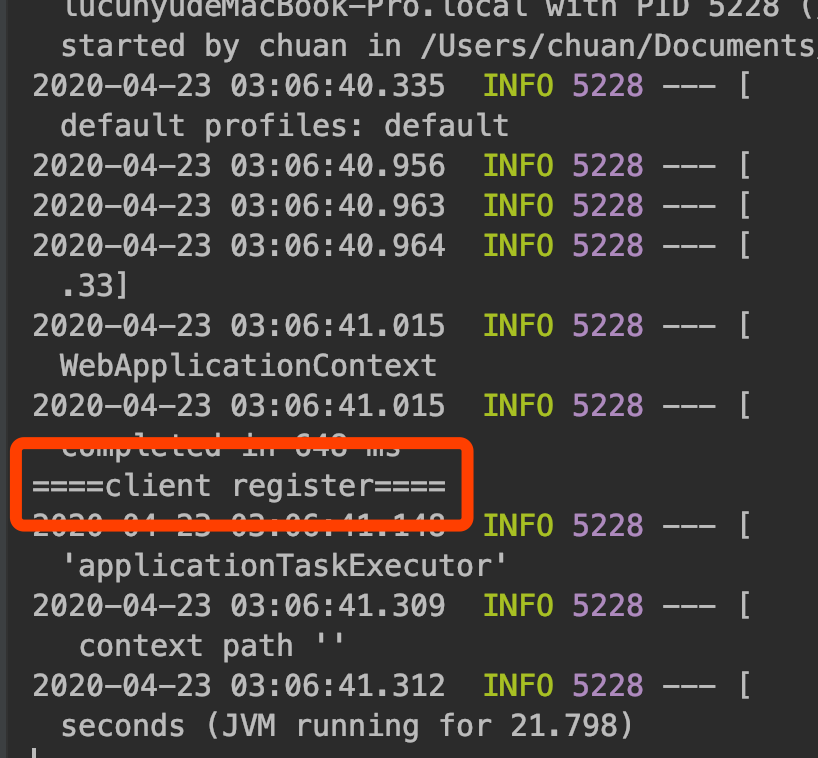
控制台打印的是我们demo工程里创建CcService实例方法内的字符串,而CcAutoConfiguration内的打印语句未执行,这是因为我们在CcAutoConfiguration类中的方法加了
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ CcService.class })来控制实例的创建。(划知识点,约定大于配置)
六、总结
通过自定义starter分析一下其工作原理:
- SpringBoot在启动时扫描项目依赖的全部jar包,并寻找
META-INF/spring.factories文件 - 根据
META-INF/spring.factories加载符合条件的AutoConfigure类 - 根据
@Conditional注解条件进行自动配置,并将Bean注入到Spring Context中。
